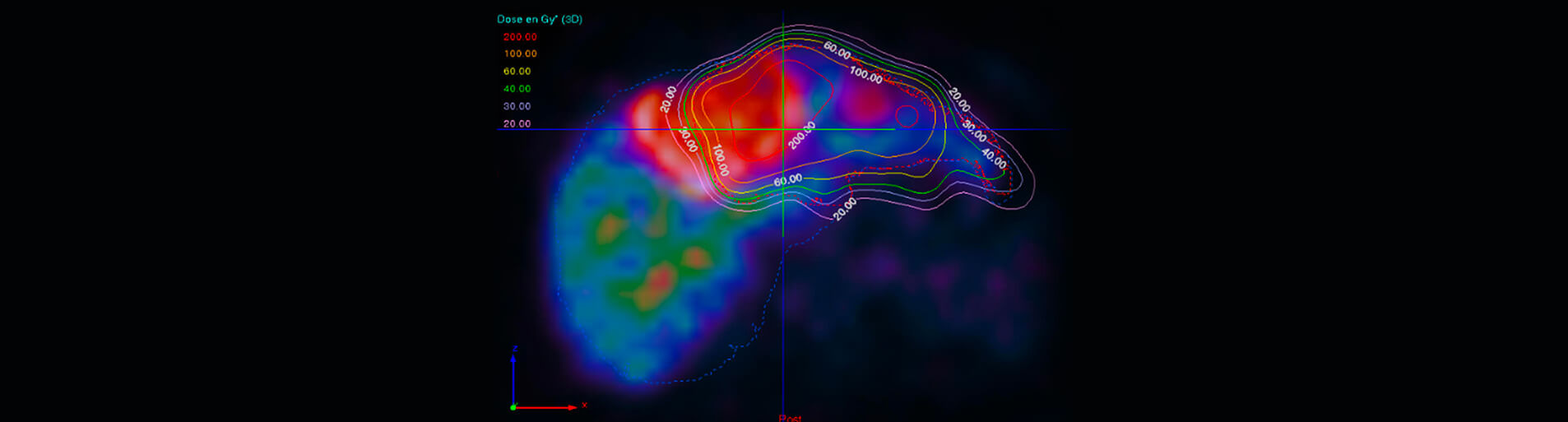
RADIOTHERANNOSTICS
The Unit is committed to advancing the development and clinical integration of novel theranostic radiopharmaceutical pairs, encompassing both diagnostic and therapeutic applications, in collaboration with the Nuclear Medicine Department of H.U.B. Our primary focus is on characterizing the imaging properties and therapeutic efficacy of radiopharmaceuticals. Utilizing state-of-the-art image processing algorithms, we develop advanced methods for the quantitative analysis of medical images derived from PET and SPECT modalities, with the aim of extracting precise quantitative information. Additionally, we specialize in accurate and precise dosimetry, employing sophisticated computational models to optimize treatment planning and minimize radiation risks. Our overarching objective is to elevate the precision and efficacy of radiotheranostic applications, thereby enhancing patient outcomes. Through close collaboration with clinical partners, we translate our research findings into clinical practice, ensuring the safe and effective implementation of novel radiotheranostic strategies. At the heart of our approach is interdisciplinary collaboration, as we engage with experts in nuclear medicine, radiology, and oncology to drive innovation in personalized medicine.
A selection of our projects:
Selected Publications:
[18F]FDG PET/CT-Avid Discordant Volume as a Biomarker in Patients with Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Multicenter Study.
Chan DL, Hayes AR, Karfis I, Conner A, et al. J Nucl Med. 65(2):185-191. (2024) doi:10.2967/jnumed.
Prediction of 177Lu-DOTATATE PRRT Outcome Using Multimodality Imaging in Patients with Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Results from a Prospective Phase II LUMEN Study.
Mileva M, Marin G, Levillain H, et al. J Nucl Med. 65(2):236-244. (2024) doi:10.2967/jnumed.123.265987.
Quantitative Lu SPECT/CT imaging for personalized dosimetry using a ring-shaped CZT-based camera.
Danieli R, Stella M, Leube J, et al. EJNMMI Phys. 10(1):64. (2023) doi:10.1186/s40658-023-00586-z.
Clinical impact of 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT-based personalized predictive dosimetry in selective internal radiotherapy: a real-life single-center experience in unresectable HCC patients.
Bucalau AM, Collette B, Tancredi I, et al. Eur J Hybrid Imaging. 7(1):12. (2023) doi:10.1186/s41824-023-00171-8.
Dual [68Ga]DOTATATE and [18F]FDG PET/CT in patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: a multicentre validation of the NETPET score.
Chan DL, Hayes AR, Karfis I, et al. Br J Cancer. 128(4):549-555. (2023) doi:10.1038/s41416-022-02061-5.
International recommendations for personalized selective internal radiation therapy of primary and metastatic liver diseases with yttrium-90 resin microspheres.
Levillain H, Bagni O, Deroose CM, et al. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 48(5):1570-1584. (2021) doi:10.1007/s00259-020-05163-5.
Combined quality and dose-volume histograms for assessing the predictive value of 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT simulation for personalizing radioembolization treatment in liver metastatic colorectal cancer.
Levillain H, Burghelea M, Derijckere ID, et al. EJNMMI Phys. 7(1):75. (2020) doi: 10.1186/s40658-020-00345-4.
Prognostic value of a three-scale grading system based on combining molecular imaging with 68Ga-DOTATATE and 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasias.
Karfis I, Marin G, Levillain H, et al. Oncotarget. 11(6):589-599. (2020) doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27460.
The metabolic clinical risk score as a new prognostic model for surgical decision-making in patients with colorectal liver metastases.
Duran Derijckere I, Levillain H, Bohlok A, et al. J Surg Oncol. 121(2):350-356. (2020) doi: 10.1002/jso.25763.
Personalised radioembolization improves outcomes in refractory intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicenter study.
Levillain H, Duran Derijckere I, Ameye L,et al. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 46(11):2270-2279. (2019) doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04427-z.
Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) before partial hepatectomy or radiofrequency destruction for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: a feasibility and safety pilot study.
Lemaire M, Lucidi V, Bouazza F, et al. HPB (Oxford). 20(7):641-648. (2018) doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.01.006.
A dosimetry procedure for organs-at-risk in 177Lu peptide receptor radionuclide therapy of patients with neuroendocrine tumours.
Marin G, Vanderlinden B, Karfis I, et al. Phys Med. Dec;56:41-49. (2018) doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2018.11.001.
A selection of our projects:
- Dose-Response Modelling for Nephrotoxicity: A Comparative Study of 177Lu and 161Tb-DOTATATE
- Advancements in Radioligand Therapy with 177-Lutetium
- Selective Internal Radiotherapy via Transarterial Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 or Holmium-166 Microspheres: Advancements in Personalized Dosimetry
Selected Publications:
[18F]FDG PET/CT-Avid Discordant Volume as a Biomarker in Patients with Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Multicenter Study.
Chan DL, Hayes AR, Karfis I, Conner A, et al. J Nucl Med. 65(2):185-191. (2024) doi:10.2967/jnumed.
Prediction of 177Lu-DOTATATE PRRT Outcome Using Multimodality Imaging in Patients with Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Results from a Prospective Phase II LUMEN Study.
Mileva M, Marin G, Levillain H, et al. J Nucl Med. 65(2):236-244. (2024) doi:10.2967/jnumed.123.265987.
Quantitative Lu SPECT/CT imaging for personalized dosimetry using a ring-shaped CZT-based camera.
Danieli R, Stella M, Leube J, et al. EJNMMI Phys. 10(1):64. (2023) doi:10.1186/s40658-023-00586-z.
Clinical impact of 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT-based personalized predictive dosimetry in selective internal radiotherapy: a real-life single-center experience in unresectable HCC patients.
Bucalau AM, Collette B, Tancredi I, et al. Eur J Hybrid Imaging. 7(1):12. (2023) doi:10.1186/s41824-023-00171-8.
Dual [68Ga]DOTATATE and [18F]FDG PET/CT in patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: a multicentre validation of the NETPET score.
Chan DL, Hayes AR, Karfis I, et al. Br J Cancer. 128(4):549-555. (2023) doi:10.1038/s41416-022-02061-5.
International recommendations for personalized selective internal radiation therapy of primary and metastatic liver diseases with yttrium-90 resin microspheres.
Levillain H, Bagni O, Deroose CM, et al. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 48(5):1570-1584. (2021) doi:10.1007/s00259-020-05163-5.
Combined quality and dose-volume histograms for assessing the predictive value of 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT simulation for personalizing radioembolization treatment in liver metastatic colorectal cancer.
Levillain H, Burghelea M, Derijckere ID, et al. EJNMMI Phys. 7(1):75. (2020) doi: 10.1186/s40658-020-00345-4.
Prognostic value of a three-scale grading system based on combining molecular imaging with 68Ga-DOTATATE and 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasias.
Karfis I, Marin G, Levillain H, et al. Oncotarget. 11(6):589-599. (2020) doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27460.
The metabolic clinical risk score as a new prognostic model for surgical decision-making in patients with colorectal liver metastases.
Duran Derijckere I, Levillain H, Bohlok A, et al. J Surg Oncol. 121(2):350-356. (2020) doi: 10.1002/jso.25763.
Personalised radioembolization improves outcomes in refractory intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicenter study.
Levillain H, Duran Derijckere I, Ameye L,et al. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 46(11):2270-2279. (2019) doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04427-z.
Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) before partial hepatectomy or radiofrequency destruction for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: a feasibility and safety pilot study.
Lemaire M, Lucidi V, Bouazza F, et al. HPB (Oxford). 20(7):641-648. (2018) doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.01.006.
A dosimetry procedure for organs-at-risk in 177Lu peptide receptor radionuclide therapy of patients with neuroendocrine tumours.
Marin G, Vanderlinden B, Karfis I, et al. Phys Med. Dec;56:41-49. (2018) doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2018.11.001.
